As everywhere in the human body, cysts can develop on the ovaries. The vast majority of ovarian cysts are benign. Depending on the case, they can either be monitored or removed.
Types of Ovarian Cysts
There are two main types of ovarian cysts. Hormonal cysts, also called “functional”, and non-hormonal cysts, also called “organic”.
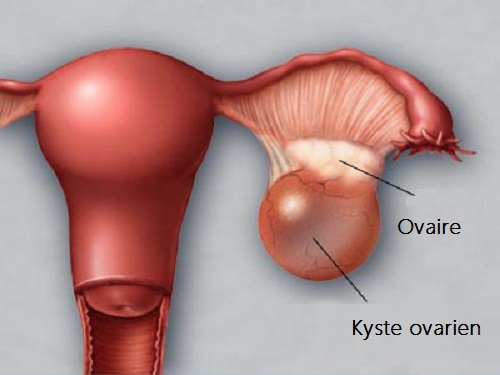 Functional Cysts
Functional Cysts
Functional cysts generally occur in patients who do not use hormonal contraception. Under the effect of the patient’s natural hormones, a small fluid-filled sac, a few centimeters in size, forms within the ovary. This sometimes goes completely unnoticed and is discovered during an ultrasound. It can also lead to various issues such as lower abdominal pain, menstrual irregularity, and pain during sexual intercourse. These cysts usually resolve on their own after 2 to 3 cycles. Sometimes, taking birth control pills for 2 to 3 months to allow the ovaries to rest proves useful.
Organic Cysts
These are cysts that, by definition, will not resolve on their own. Very often benign, they are most commonly removed surgically via laparoscopy. Depending on their nature, they are classified as dermoid cysts, cystadenomas, and endometriomas.
Further Tests
Ovarian cysts are generally diagnosed by ultrasound. MRI and blood tests are sometimes useful to determine their structure, location, and size. However, only their analysis after removal will definitively reveal their true nature.
Laparoscopic Cyst Removal
Ovarian cystectomy is the name given to the surgical removal of an ovarian cyst. If the woman is of childbearing age and the cyst is benign, only the cyst is removed to preserve fertility. If the woman is post-menopausal, a total removal of the ovary and fallopian tube is most often performed to prevent cyst recurrence.
The surgical removal of an ovarian cyst is a surgical procedure performed under general anesthesia by a gynecological surgeon. This operation can be performed in two ways: either by laparoscopy or, exceptionally, by laparotomy. Laparoscopy is the preferred technique for cysts that appear benign. The cyst is removed through micro-incisions of a few millimeters in the lower abdomen, under the guidance of a camera inserted through the navel. Laparotomy involves opening the abdomen in a traditional manner and is mainly used for hard and voluminous cysts or in cases of ovarian cancer.
Post-operative Course
The operation for the surgical removal of an ovarian cyst lasts less than an hour and is most often performed as an outpatient procedure. Sometimes, an overnight stay for observation in the hospital may be useful. Upon discharge, a work leave is recommended for a duration ranging from 1 to 2 weeks.
Simple pain medication is prescribed, and a post-operative consultation appointment is scheduled approximately 3 weeks after the operation.




Leave A Comment